There is no standard downpipe size in the UK and downpipes in the UK for residential homes and commercial properties alike are made of various different materials, including PVC, cast-iron, stainless steel, zinc, copper, and aluminium. Note: Rainclear only sell metal systems. The location of the property and the roof size and pitch of the roof will dictate which are the correct size for you to install to maintain a property free from water damage and the resulting rot and mould.

As extraordinary weather patterns become ever more regular with intense rain storms causing major challenges for rainwater disposal. This guide provides a basic method for calculating flow requirements or ‘flow capacity’ and therefore the required gutter and downpipe size.
Step 1: Geographical Location and Rainfall Intensity Maps
Rainfall intensity can vary greatly based on geographical location and is crucial for flow capacity calculations. British Standard BS EN 12056-3: 2000 contains maps showing rainfall intensity in litres/second per m2 for 1, 5, 50 and 500 year storms of 2 minute duration. (All external gutters designed for 1 year event).
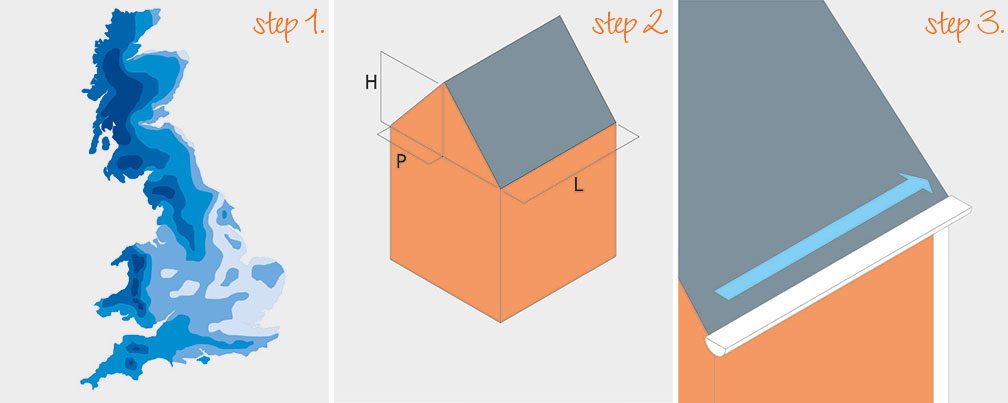
Step 2: Calculating Catchment Area
Using this formula CA = (P+H/2) x L
Where: CA = Catchment area in square metres
P = Horizontal distance between eaves and ridge
H = Height of roof
L = Length of eaves
Step 3: Frequency and Positioning of outlets/downpipes
Calculate the number of outlets per run.
It is the roof area, the pitch of the roof and the number of ‘drops’ (downpipes coming down from outlets in the guttering around the building) determine the flow – we will need to know these to calculate the flow capacity for you. Accurate calculations of the effective roof area is essential for an effective drainage system.
Step 4: Calculate Flow Rate Requirements
Overall rainfall : Catchment area (CA) x Rainfall intensity (RI) = Overall Rainfall (OR).
Flow rate per outlet : Overall rainfall (OR) ÷ Number of outlets = Flow rate per outlet. Choose gutter/outlets and downpipe diameters according to published flow rate capacities.
For tailored advice specific to your project regarding rainwater flow calculations, reach out to our friendly and knowledgeable team for free at 0800 644 44 26.
Or email us for help with a flow calculation[email protected]
Downpipes come in two shapes: square and round. Rainclear supply them both in most metals.
What is the sizing of downpipes?
Square downpipes typically range in size from 60mm to 100mm, including specific sizes like 100 x 75mm (4″x3″) for Cast Iron square downpipes , 75x75mm (3″x3″) and 100 x 75mm (4″x3″) for heritage ‘cast’ Aluminium Square downpipes, and 76x76mm for the more modern swaged square aluminium downpipes.

Round downpipes typically range in size from 60mm to 100mm.
The outer diameter (OD) is used to denote the size of downpipes. Measuring the downpipe diameter is crucial for ensuring accurate replacements/installations.
Measuring the circumference of a downpipe helps to calculate its outer diameter. To find the outer diameter of a round downpipe, divide the circumference by 3.14 (π). Square downpipes are measured easily by measuring one side with a ruler. Downpipe sizes can vary significantly across different manufacturers and systems. Plastic, aluminium, zinc, and copper downpipes in the UK are approximately 2mm thick. Classical cast iron downpipes are significantly thicker, coming in at anywhere between 9mm and 13mm depending on the brand.

Many downpipe options have varying lengths. The traditional heritage materials come in 6 foot lengths while the modern materials ranges come in 3mtre lengths.
3P Technik downpipe diverters are designed to fit a range of non-cast iron downpipes.
Rainclear also supply diverters to match the metal ranges of downpipes we supply, including cast iron ones.

